FemoroAcetabular Impingement (FAI): A Brief Summary & The Role Of Physiotherapy
What is FAI?
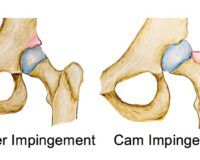
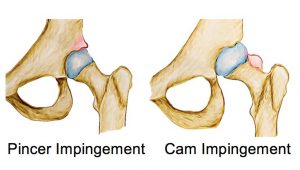
FAI is a movement related condition which causes pain either in the hip joint, groin, lower back, buttock or thigh. FAI can be classified into 3 groups:
- Pincer impingement: where abnormal bone spurs alter the shape of the pelvis
- CAM impingement: where the upper aspect of the thigh bone lacks a spherical shape where it attaches to the pelvis
- Mixed: combination of both of the above
Over time these structural changes can cause damage to the cartilage of the hip socket (acetabulum) and can therefore, if chronic, lead to osteoarthritis and degenerative changes.
Surgical treatment
In some cases, surgical management may be indicated in order to improve the connection between the thigh bone and the pelvis and ensure an even surface of these joints. Scans of the hip/s should be performed prior to discussing surgical treatment (e.g. X-Ray or MRI scan). Physiotherapists can help individuals by communicating to a trusted referral partner/orthopaedic surgeon if necessary.
Pre & post-surgical rehab
Physiotherapy can play a very important role in the prehabilitation and post surgery rehabilitation for FAI.
Typically prehab will involve strengthening of the hip joint and surrounding musculature, improving neuromuscular control, improving mobility of the hip joint and will involve education regarding what management may look like for the individual following surgery. This may be addressed during individualised pilates classes.
Typically, post-op rehab will involve manual therapy (e.g. key trigger points, lower back mobilisation) and prescription of gentle home exercises. Starting at ~ 6-8 weeks post-surgery, functional and sport-specific drills will be addressed to prepare the individual for return to sports/activity, along with an individualised pilates program.
Key messages
- Younger individuals participating in sports such as football and soccer are most likely to experience FAI pain due to the physical demands.
- Jumping, kicking (in front and across your body) and twisting/turning should be avoided as these will likely flare-up symptoms.
- Pain/symptoms can be experienced in the hip joint, groin, back, buttock and thigh (and may include catching/clicking).
- Conservative physiotherapy treatment can be very effective in reducing symptoms and plays a significant role in pre and post-op rehab
- Surgical management may be required to correct joint alignment
None of the information in this article is a replacement for proper medical advice. Always see a medical professional for advice on your injury.
To know more about hip soreness and to get an assessment, book to see one of our Practitioners (Physiotherapist, Massage Therapist) through our website www.therapia.com.au or via https://therapia-physiotherapy-pilates.cliniko.com/bookings